CO582: Computer Interaction and User Experience
Interacting with AI systems
Tomas Petricek
email: t.petricek@kent.ac.uk
twitter: @tomaspetricek
office: S129A
Interacting with AI systems
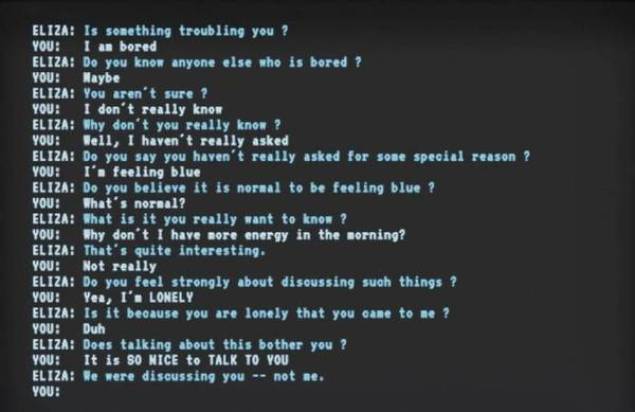
ELIZA (1964)
Written by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT
To demonstrate that the communication between man and machine was superficial
Eliza: The AI psychotherapist
1. Looks for simple patterns in text

2. Replace words to form a question

Eliza: The AI psychotherapist

Surprisingly effective
Weizenbaum's own secretary asked Weizenbaum to leave the room so that she and ELIZA could have a real conversation.
Weizenbaum's commentary
I had not realized (..) that short exposures to a simple
computer program could induce powerful
delusional thinking in quite normal people."

Unintended consequences of Artificial Intelligence
We know how it works technically...
But no idea how it works in the world!
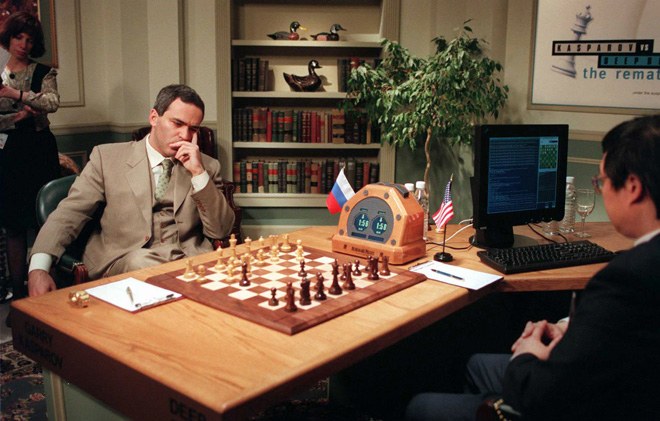

Deep Blue vs Gary Kasparov (1997)
First computer to beat a world champion.

Advanced Chess
(since 1998)
Can a computer program complement a human?
Human thinking
State space search
Interacting with AI systems
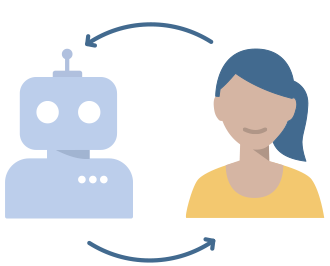
Automation or symbiosis?
- Computers will replace humans!
- Can computers assist humans instead?
- What is more beneficial for whom?
How users think about AI systems
- Anthropomorphic metaphor is misleading
- Can we understand how AI systems decide?
- Can AI systems be creative?
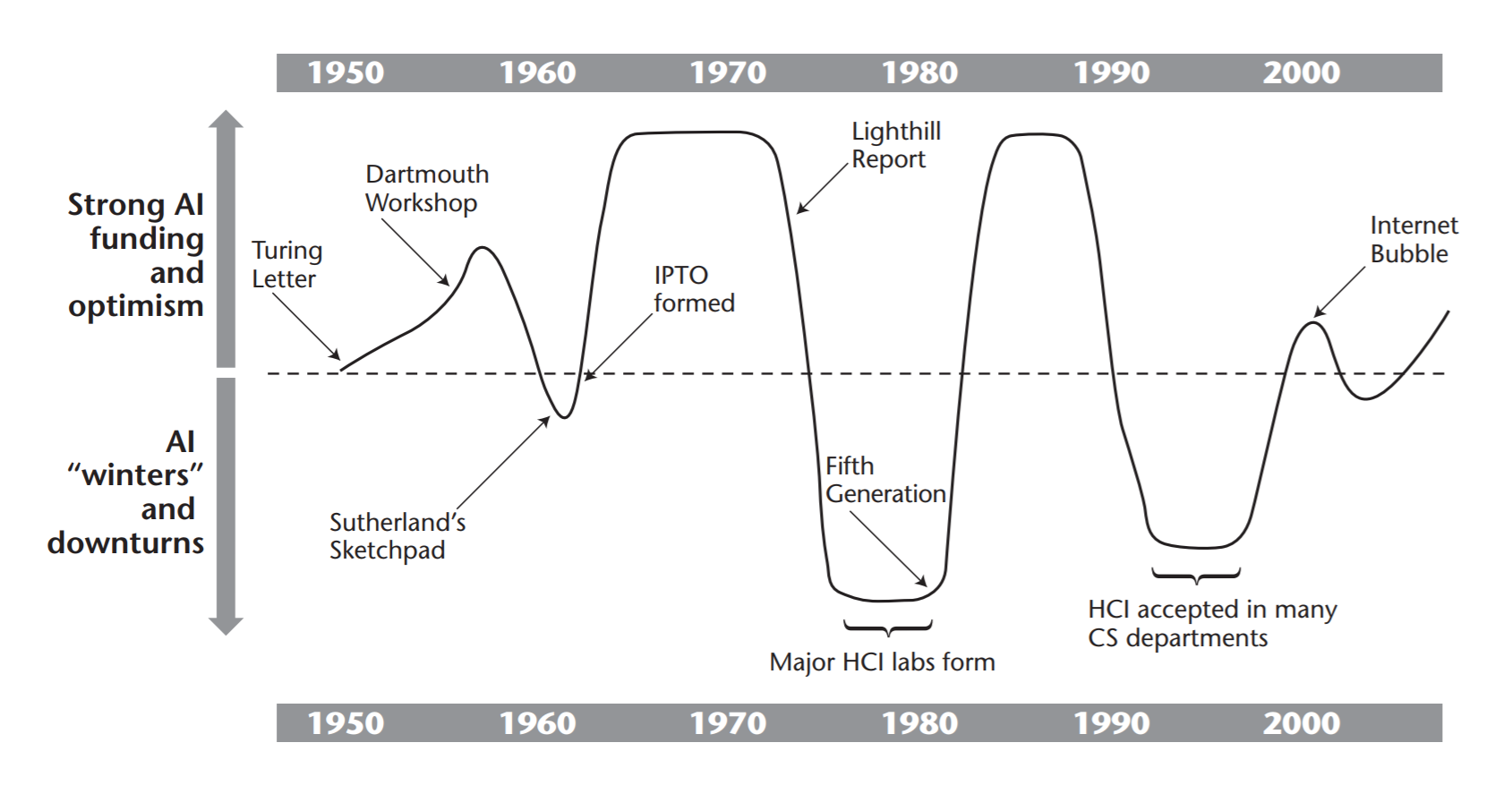
Should we expect new wave of HCI soon?
Perhaps accidentally, AI winters are HCI summers!
Human in the loop
Human in the loop data science
Data science tasks
- Cleaning and processing data
- Classifying or identifying objects
- Whenever it's mission critical
Human and computer
- AI can generalize from samples
- AI can offer a range of suggestions
- Human corrects and gives good samples
Trifacta Wrangler
Combining UX and AI techniques for generating data extraction scripts
Trifacta Wrangler
Human in the loop data cleaning
Human computer symbiosis
User provides examples to refine answer
AI attempts to fit model to samples
Model is readable source code

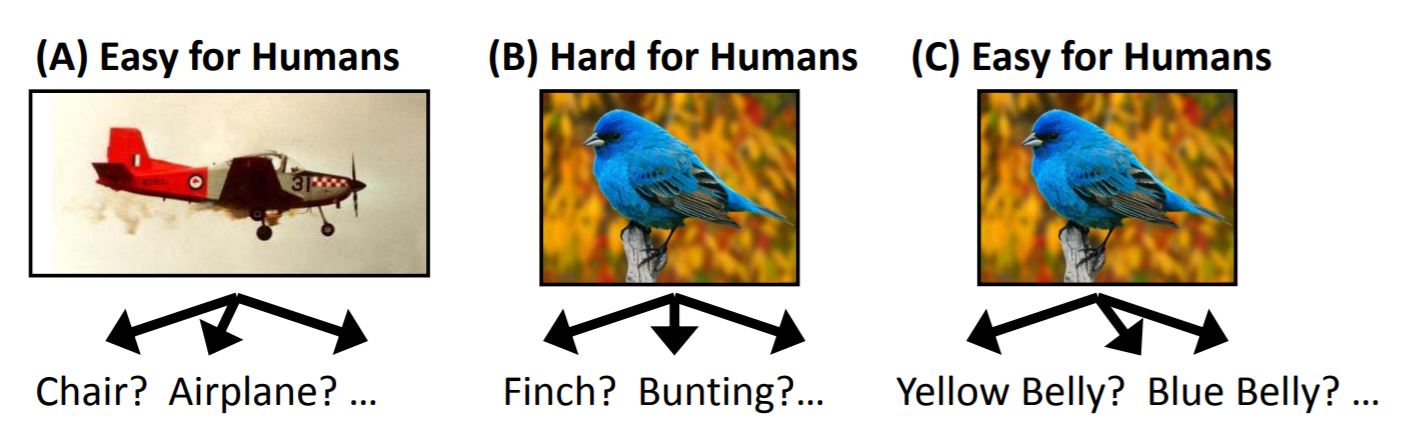
Visipedia
Human in the loop for image recognition
AI asks for help, using questions easy for human
Visipedia
Human in the loop image recognition
Human computer symbiosis
Humans are good at recognizing key features
Computers can efficiently search
Dialog metaphor for the interaction
Explainable AI
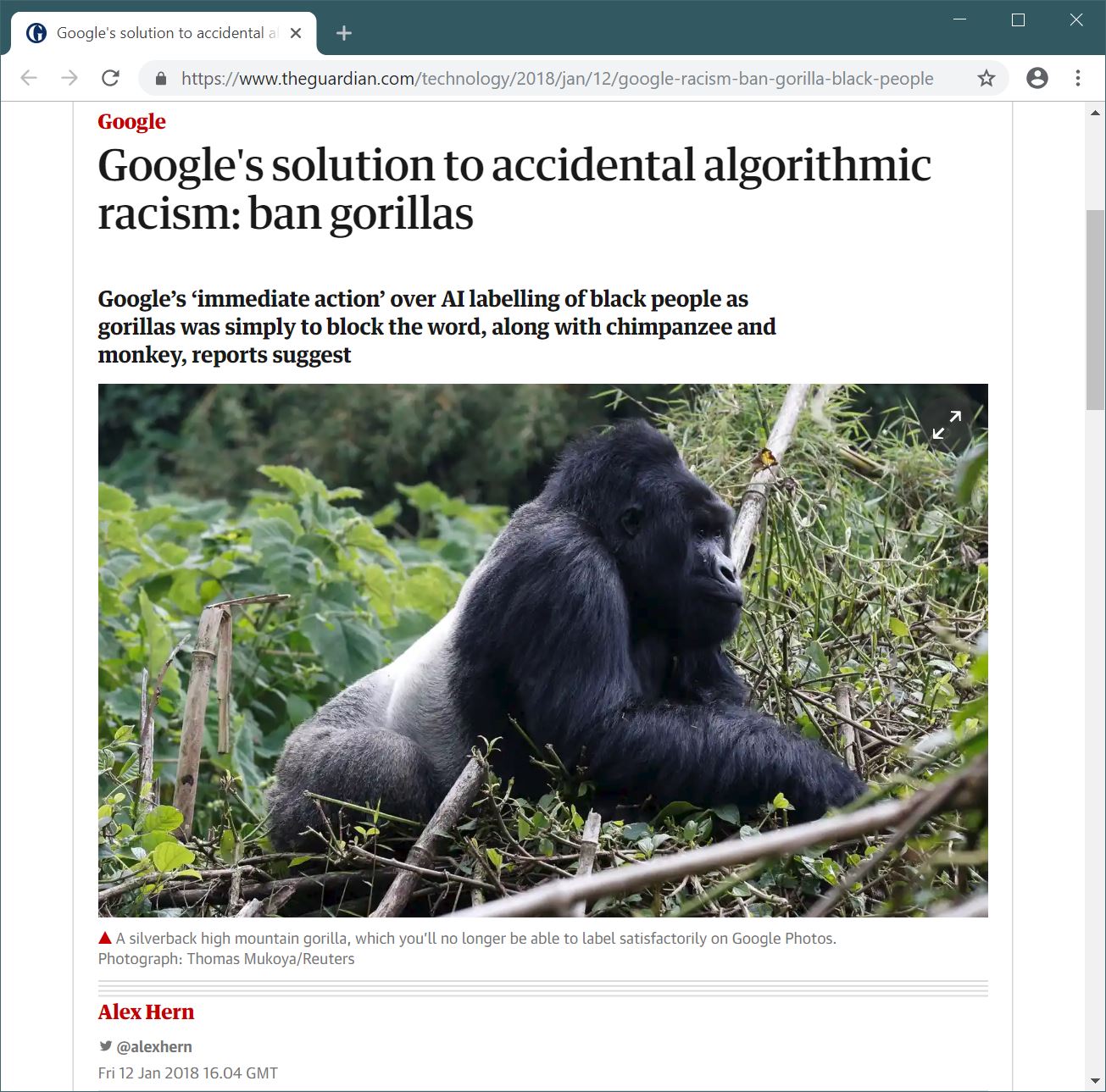
Racist Google Photos
Example of biased AI
What is the reason why the app does this?
What was the training data used by Google?
How to avoid this?
Why explainability matters

Right to explanation
- Right to obtain an explanation of a de-cision based on automated processing
- What does explanation mean?
Explainable AI and user interaction
- Interacting with models inferred from big data
- Can user understand the system?
- Not easy for modern neural nets
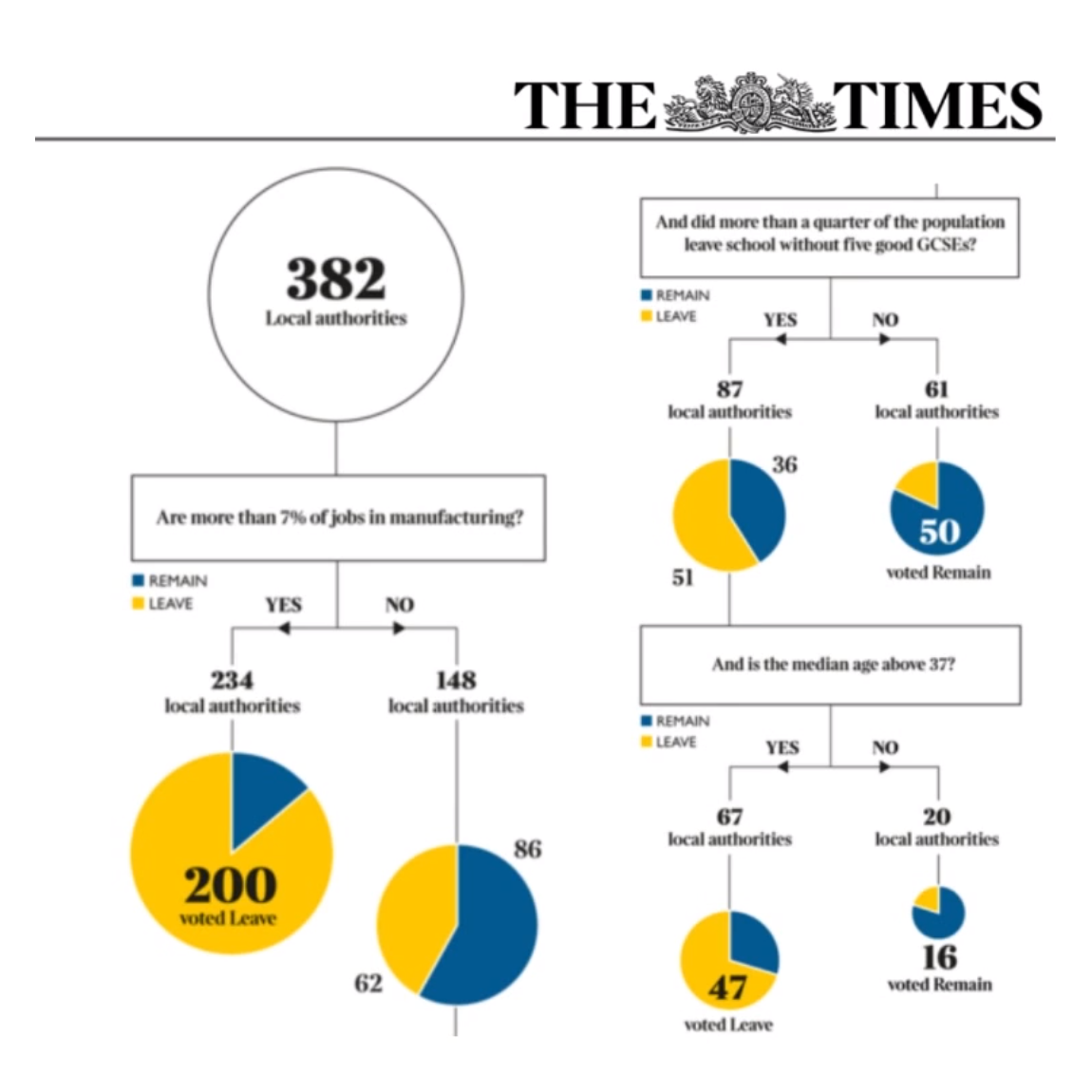
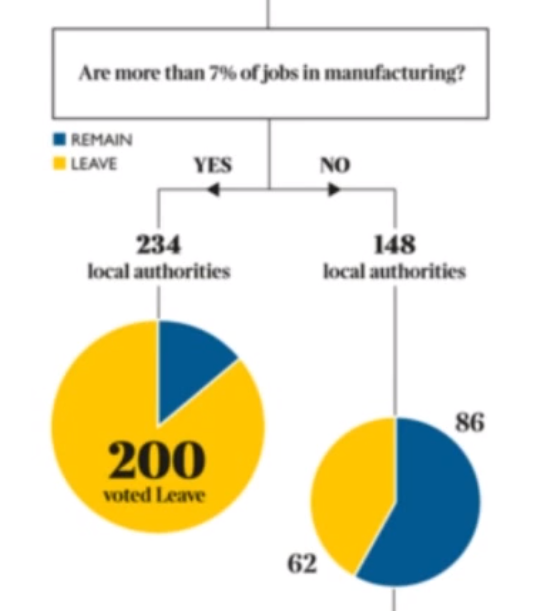
How Britain Voted
The Times
Using decision trees to map the structure of the Brexit referendum
Different kinds of AI models
Statistical models
- Work great in practice!
- All we know are the weights
- Not much we can do with them
Explicit logical model
- Produce an interpretable structure
- Decision trees, if-then rules
- Can be further manipulated by user
Challenges posed by modern AI methods
Design considerations when creating AI systems
Agency and training data sets
Programming by example such as Wrangler
The nature of human and AI reasoning styles
Legal status of non-symbolic intellectual property
Can AI systems be creative?
Can AI systems be creative?
User experience and artificial creativity
What does it mean to be creative?
Does output look like a result of creative action?
Is computer following creative processes?
How do users interact with the system?

Deep style transfer
Using machine learning to change image style
Looks pretty, but is there any creativity behind the system?

The Drawing Fool
Software that explains
its artistic decisions
Uses newspaper to decide mood, AI for drawing and
AI for reflection
Rethink human-centric notion of creativity
AI creativity as a human-computer interaction problem
Computers and creativity
- What comes from the programmer?
- What comes from the algorithm?
Why explanation matters
- Creativity is user experience question
- Humans expect human reasoning
- How do we know program is creative?
AI for user interfaces
Tensions between HCI and AI
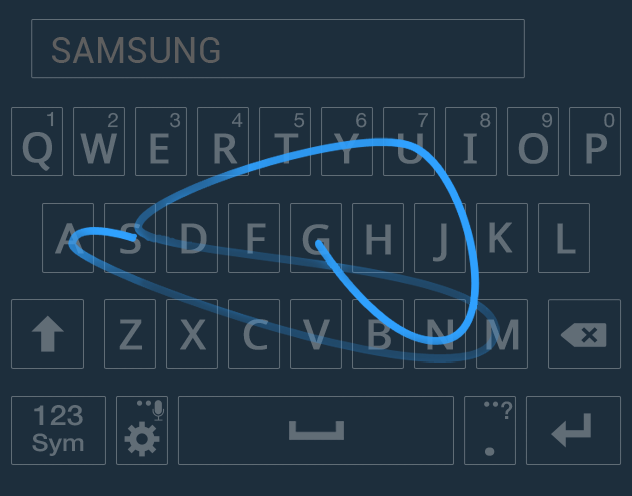
The problem with AI
Shneiderman (1989) has argued that AI in interfaces reduces predictability, which is essential for usability.
AI in user interfaces
- Handwriting recognition
- Predictive and swipe keyboards
- Speech recognition and chatbots
AI in user interfaces
Format shapes the style of interaction
Phones changes what we can fit on the screen
Motion sensing introduced new kinds of games
Chatbots (try to) make computers easier to use
Voice recognition allows hands-free interactions



Mobile text-entry methods
T9 predictive text
One key for three letters
Graffiti for Palm OS
Letter recognition
Predictive keyboards
Guess word from a stroke
Intelligent text entry methods

Principles of AI for text entry
-
Minimize the amount of information that
user needs to provide - Exploit language redundancies
User experience questions
- What is the most efficient method?
- What is the learning curve?
- Usability of error correction
Summary
Different kinds of evaluation
Human in the loop data science
Ways of efficient collaboration
Dialog and programming by example
The problem of AI explainability
Avoiding bias in AI systems
Statistical and logical models
The problem of AI creativity
Creativity as a user-defined criteria
Human reasoning as an inspiration
CO582: Interacting with AI systems
What you should remember from this lecture
- Problems posed by interaction with AI systems
- Explainability in law and creative uses
- Programming by example and decision trees
Tomas Petricek
t.petricek@kent.ac.uk | @tomaspetricek
References
Papers and links
- ELIZA—a computer program for the study of natural language communication between man and machine
- On Acid Drops and Teardrops: Observer Issues in Computational Creativity
- Interacting with an inferred world: the challenge of machine learning for humane computer interaction
- Human-in-the-loop Artificial Intelligence
- Visual Recognition with Humans in the Loop
- AI and HCI: Two Fields Divided by a Common Focus
- User Interface Goals, AI Opportunities
-
Opportunities and Challenges in
Intelligent Mobile Text Entry
