CO886: Software Engineering
Source control systems
Tomas Petricek
email: t.petricek@kent.ac.uk
twitter: @tomaspetricek
office: S129A
Collaborative software development
Collaborative software development

Source control
- Track history and code versions
- Allow merging and branching
- Git, Subversion, Mercurial, etc.
Collaborative development
- Project planning and management
- Issues, milestones, docs
- GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps, ...
Git and source control
Version and history tracking systems
Keep version history because you will need to look back
Develop features independently and merge changes
Two ways of working
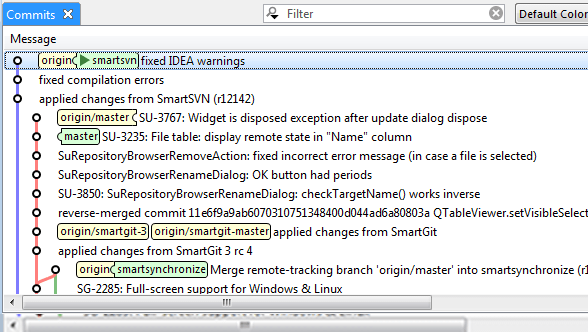
Graphical user interface
- Eclipse, VS Code, Tortoise, etc.
- Great when it works well
- Illusion of this is easy
Command line tools
- Everything using the
gitcommand - Teaches you more about how it works...
- Fortunately, easy to Google answers!
GitHub and collaboration
Help teams plan and collaborate and organize
Manage issues, notes, plans, contributions
Also a "social network"
for open source software
GitHub as a CV
Use your GitHub profile to show your work!
Great if you are looking for your first job
Valid criticism of the GitHub as a CV idea
Git and source control
Git repository
Everything in one folder
- Your regular files you can edit
.gitfolder with old versions etc..gitignoreand other special files
Versioning and collaboration
- Stage changes from files to "index"
- Save or retrieve from version history
- Push to/pull from remote repositories
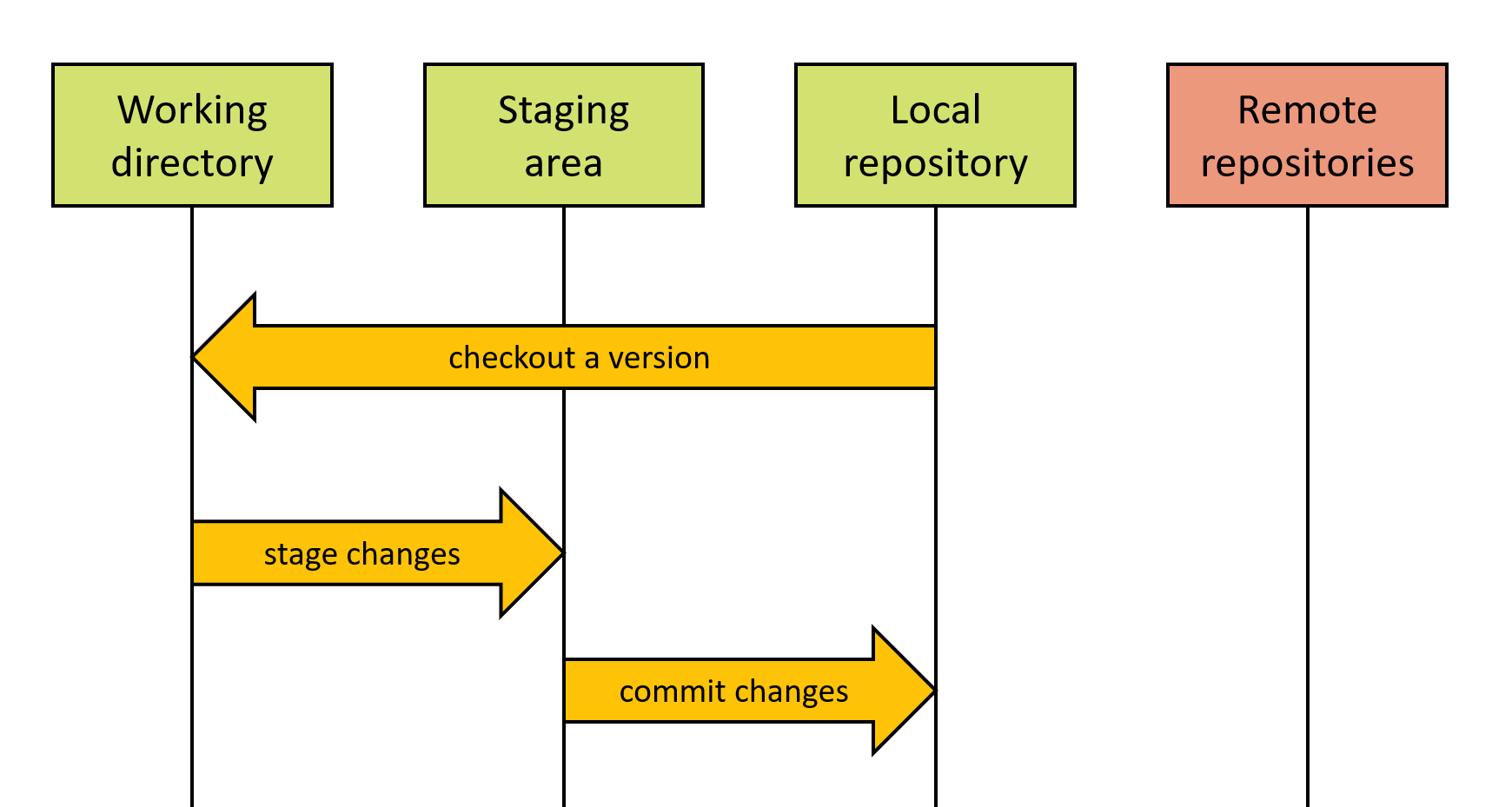
Working directory
Files you directly edit
Staging area
Selection to be archived
Local repository
History and versions
Remote repositories
Versions on other computer(s)
Creating repository and adding files (1/2)
Initialize empty repository in current folder
1: 2: |
|
Add new or modified file to the index
1: 2: 3: 4: |
|
Creating repository and adding files (2/2)
Create new version history record (commit)
1: 2: 3: 4: |
|
List the most recent history records
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: |
|
Demo: Creating repository, adding files
Using git in practice
Warning: This slide contains profanities
How to write a good commit message?
Brief summary of the change (70 characters)
Add more detailed comment after a newline
Git history and branches
Using git for versioning and features
Use branches for different versions and features
Branch is named pointer to a commit
Master branch is typically the "main" once
Branch for each version running in production
Git history and branches (1/3)
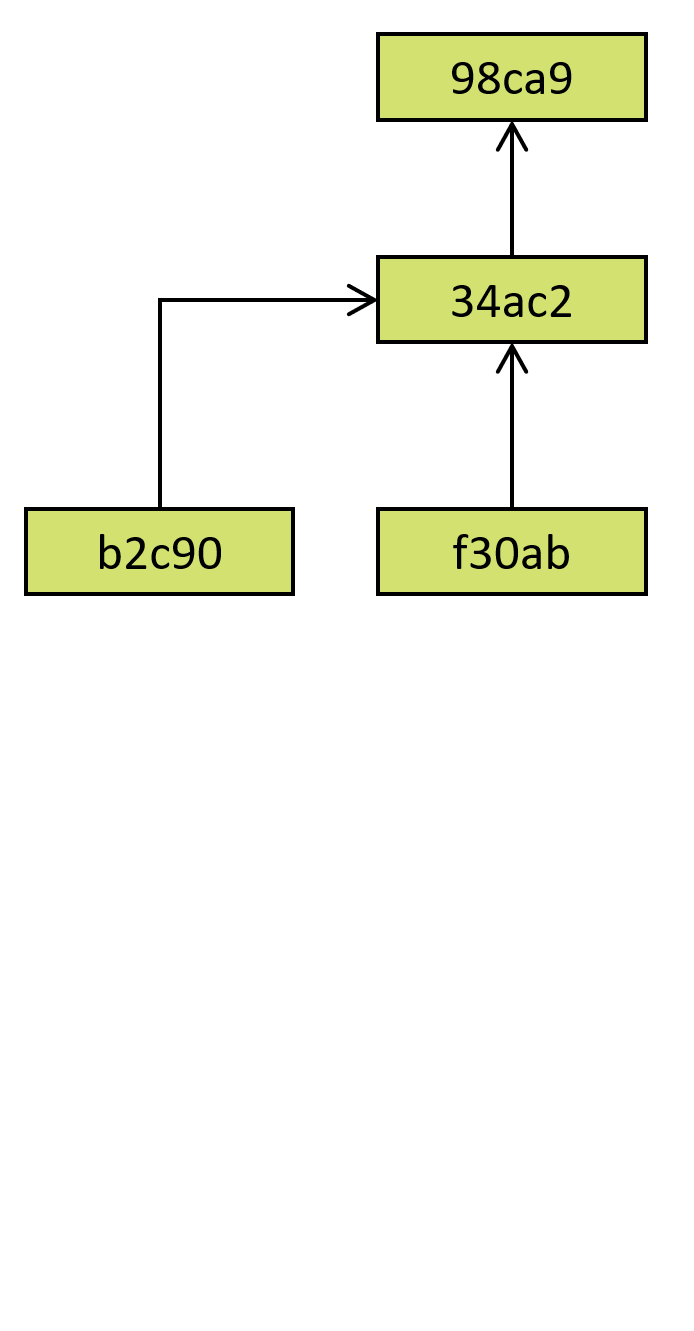
Directed acyclic graph
Commits identified by hash
Arrow to a previous state
Git history and branches (2/3)
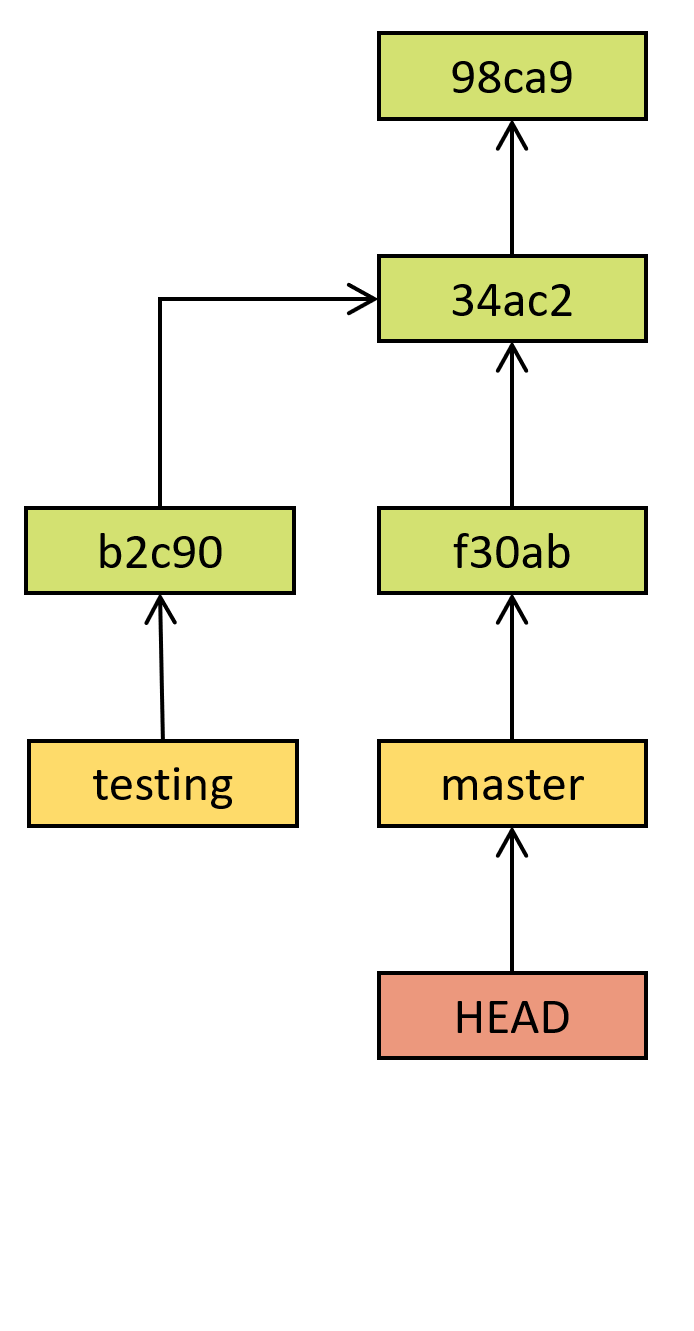
Directed acyclic graph
Commits identified by hash
Arrow to a previous state
Commits, branches, head
Branch is a pointer to commit
Current branch identified as HEAD
Git history and branches (3/3)
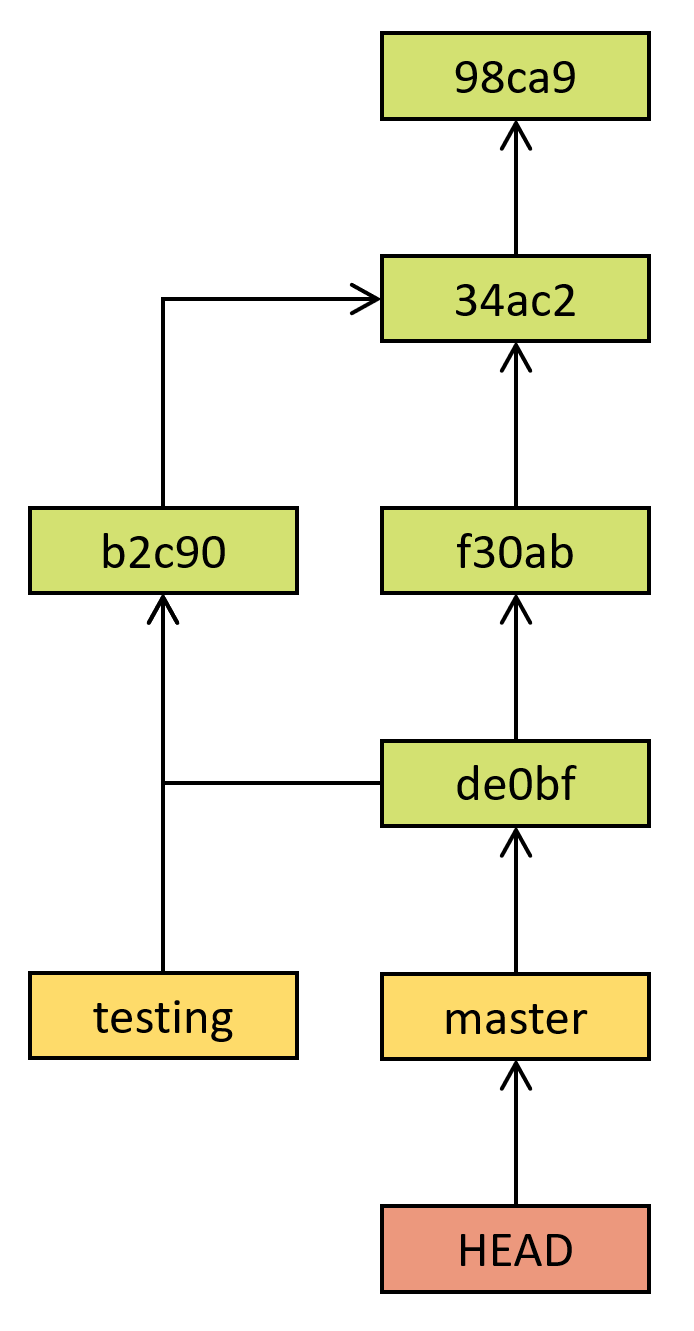
Directed acyclic graph
Commits identified by hash
Arrow to a previous state
Commits, branches, head
Branch is a pointer to commit
Current branch identified as HEAD
Merging changes from branches
Commit with multiple parents
Potential for conflicts
Working with branches (1/2)
Create and switch head to a new branch
1: 2: 3: |
|
Make a change in a new branch
1: 2: 3: |
|
Working with branches (2/2)
List branches and switch to master
1: 2: 3: |
|
Merge changes from another branch
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: |
|
Demo: Working with branches
Summary
Git and its alternatives
When is git a wrong tool and alternatives
Uses distributed model with no central server
There are user interface tools for using git
Git is way more complex than it seems
Alternatives include Subversion, Mercurial, Perforce
Source control systems
Software engineering today
From "we know where we want to get"
To "know we continue moving in the right direction"
Using git for version and history tracking
Working dir, staging area, local and remote repositories
Creating, commits, working with branches, merging
CO886: Source control systems
What you should remember from this lecture
- How git stores versions and branches
- Git commit, branch, checkout, pull, push
Tomas Petricek
t.petricek@kent.ac.uk | @tomaspetricek
