Write your own tiny programming system(s)
Why such a strange course topic?
Tomas Petricek, Charles University
tomas@tomasp.net
@tomasp.net
https://tomasp.net
https://d3s.mff.cuni.cz/teaching/nprg077


Research
Understanding & improving programming
- Programming languages, types and theory
- Interactive programming environments
- History and philosophy of computing
- Building tiny systems throughout!

Many different tiny systems!
-
PhD, University of Cambridge
Context-aware programming languages -
Microsoft Research Cambridge
F# and applied functional programming -
The Alan Turing Institute, London
Expert and non-expert tools for data science -
University of Kent, Canterbury
Principles of programming systems -
Charles University, Prague
Human-computer interaction and history


Demo
Coeffects playground
Needed "implementation" to finish my PhD!
How to show potential uses of theoretical work?
Tiny web demos of two potential applications

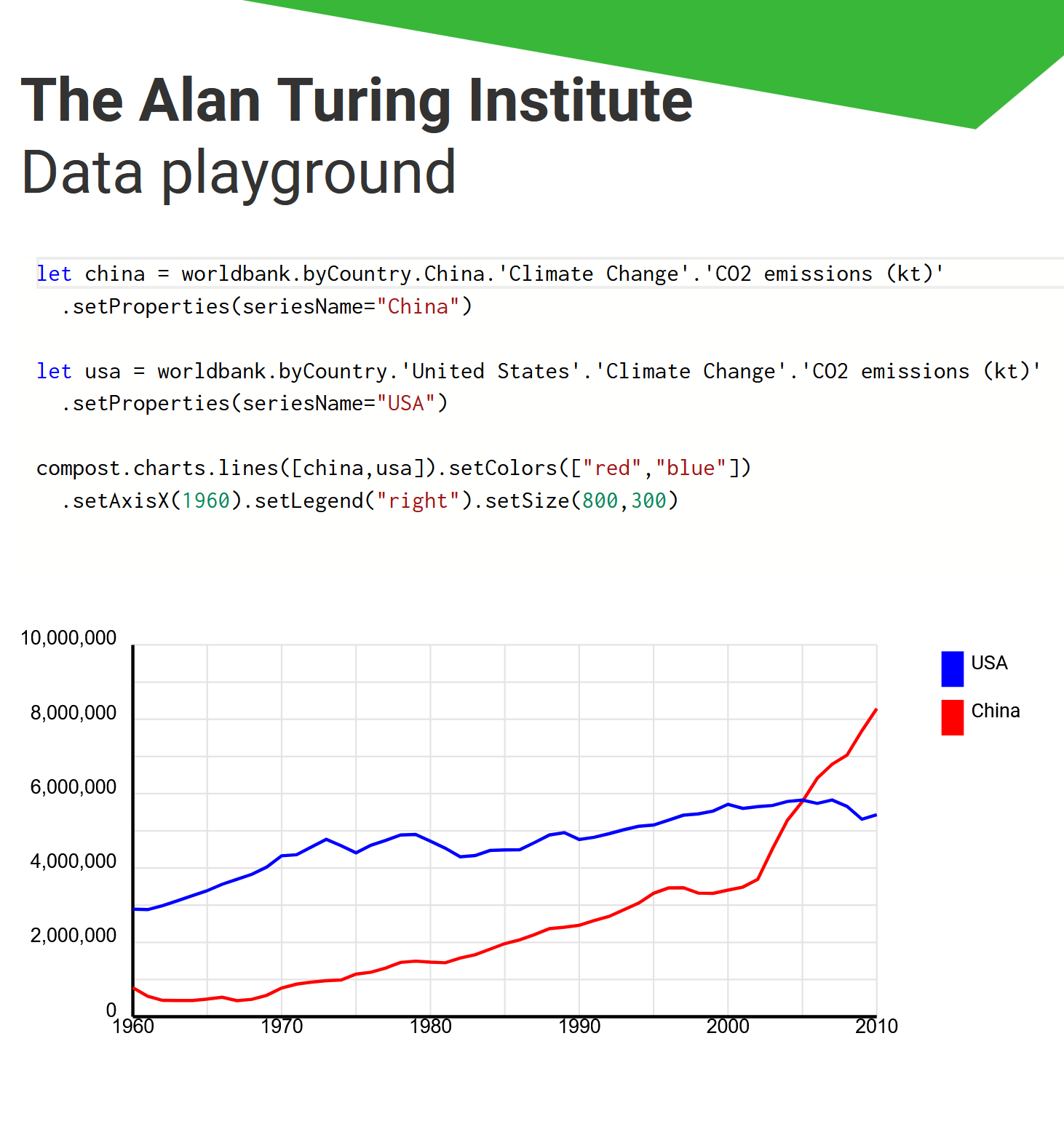
Demo
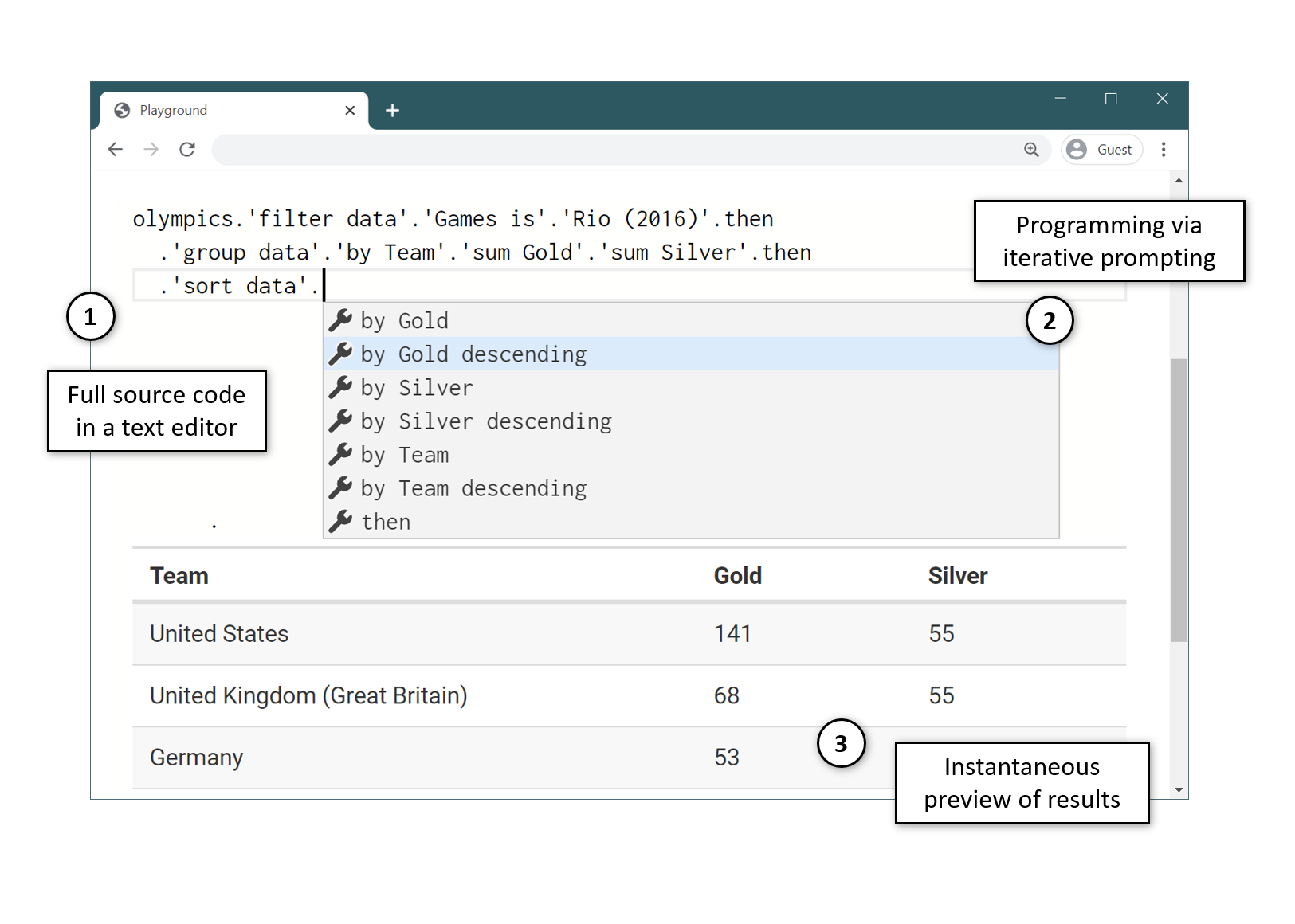
The Gamma project
Making programmatic data exploration accessible to non-programmers
Small typed language, but interaction is why it works!

Demo
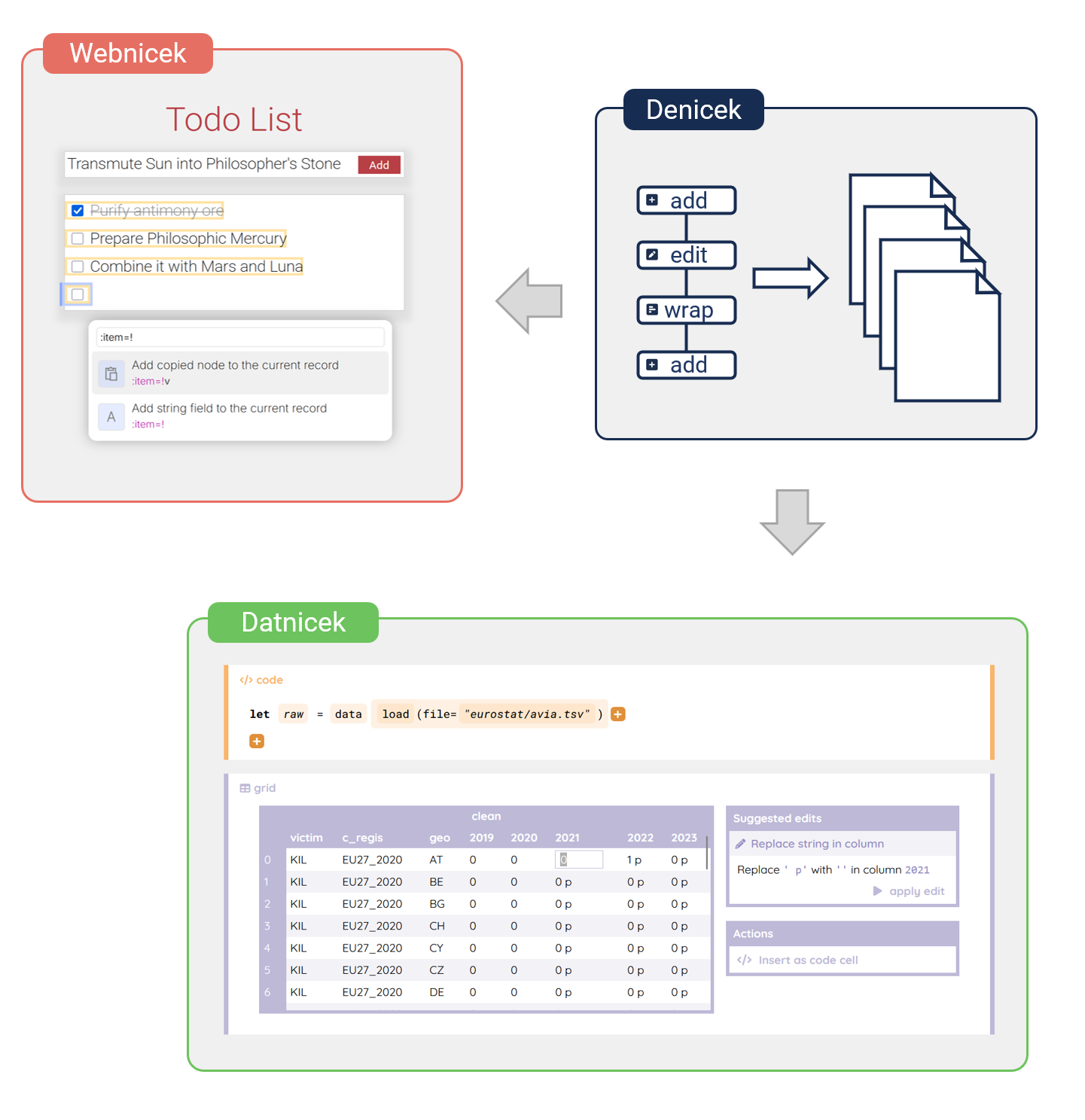
The Denicek project
Computational substrate for end-user programming
Making implementation of end-user programming experiences easier...

Practical details

Course structure
- Videos to watch in advance
- Hands-on 3-hour labs
- Code skeleton with detailed comments
Doing the course
- Six different languages or systems
- Come to the labs to get help!
- Complete basic tasks for 4/6 systems


PRG*PRG / Prague
Programming systems & languages research
D3S at MFF CUNI
PRL at FIT CTU
Ask us about PhD & post-doc opportunities!

Write your own tiny programming system(s)
Tiny systems as a methodology
Tomas Petricek, Charles University
tomas@tomasp.net
@tomasp.net
https://tomasp.net
https://d3s.mff.cuni.cz/teaching/nprg077


Academic research

What are we trying to study?
- Basic essential principles
- In isolation from other factors
- You have to ignore a lot!
What to ignore in programming?
- Efficient implementation?
- Wide-spread user adoption?
- User interface of editor tools?


Programming language theory
Ignore implementation and practical features
Prove that the core idea is formally sound

Human-computer interaction (HCI)
Ignore inner working and implementation
Show that users can actually use it and how

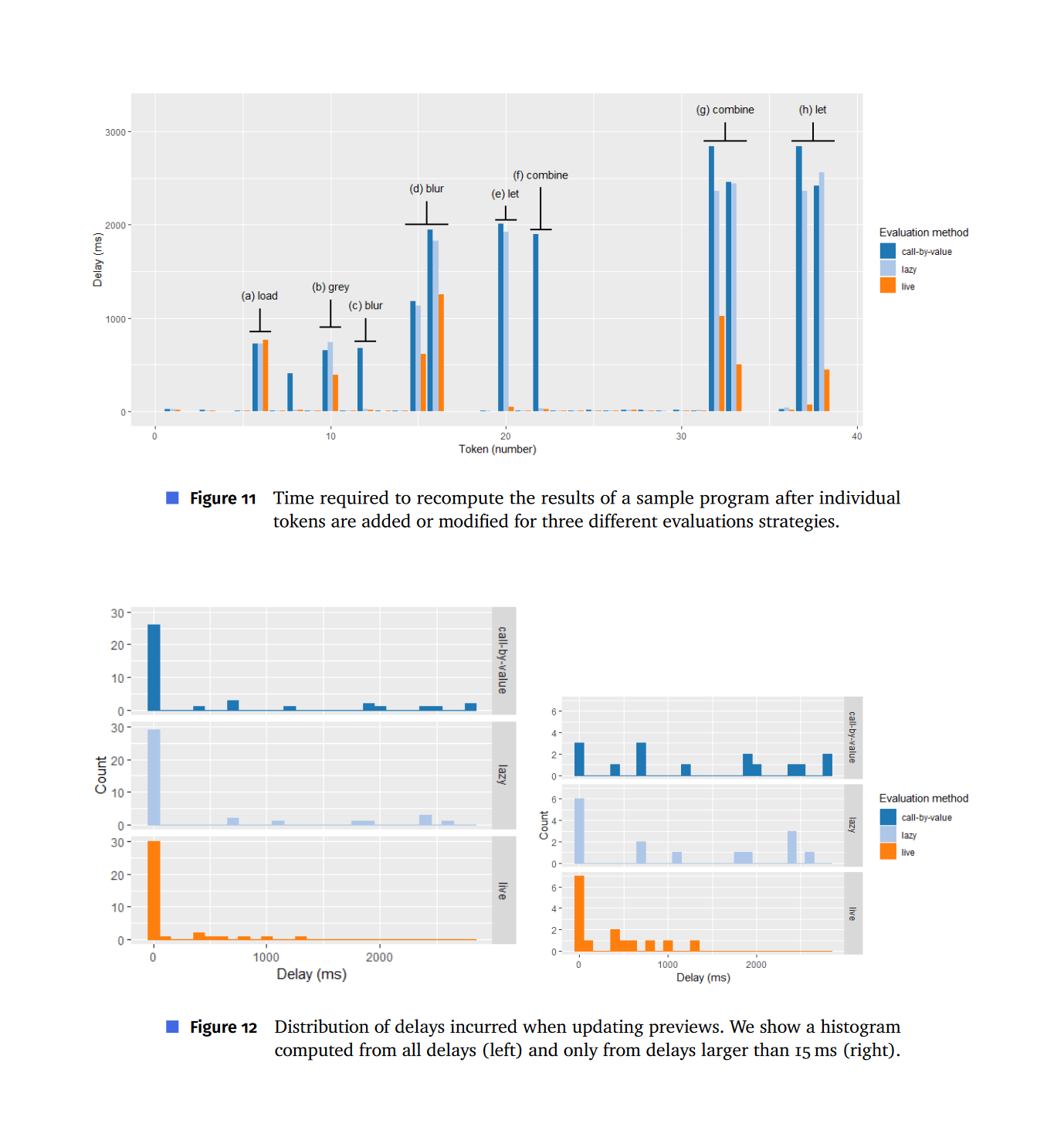
Performance evaluation
Ignore usability and design implications
Show that you can do better than a baseline

Tiny systems
What is not covered?
- Syntax choices and writing parsers
- Compilation and JIT-based runtimes
- Formal semantics and correctness
- Supporting real-world use cases

Tiny systems
What can we study?
- Can talk about stateful interactive systems
- Implement key aspects of inner working
- Reconstruct interesting past systems
- But cannot be printed on 12 pages of A4

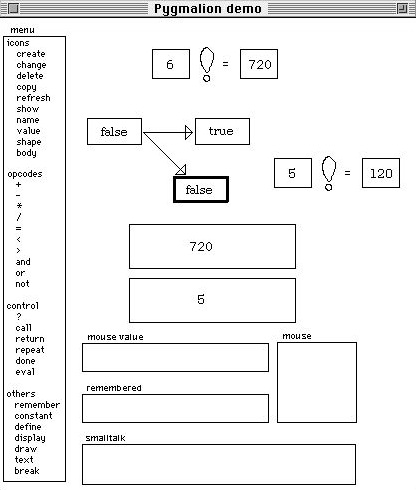
Demo
Pygmalion
Why study 1908s programming systems?
No code programming!
First us of an "icon"!

Two uses of tiny systems
Education
Best way to learn?
Write it on your own!
Understand principles
As well as subtle details
I hope you'll have fun!
Little may be enough...
Research
Imagine new paradigms
End-user programming?
Focus on interaction
How exactly did it work
Ignore practical details
They can often wait!


Teaching tiny systems
(Kamin, 1990)
Used in multiple
courses worldwide
Examples in Pascal
Languages covered are APL, Clu, LISP, Prolog, Smalltalk, Scheme, SASL
Not always focused
on the key aspect


Tiny systems and AI
(Schank, Riesbeck, 1981)
Miniature implementations of 5 Yale AI lab programs
Faster, more efficient, easier to understand, modify and extend
"Miniatures, demos and artworks" by Warren Sack

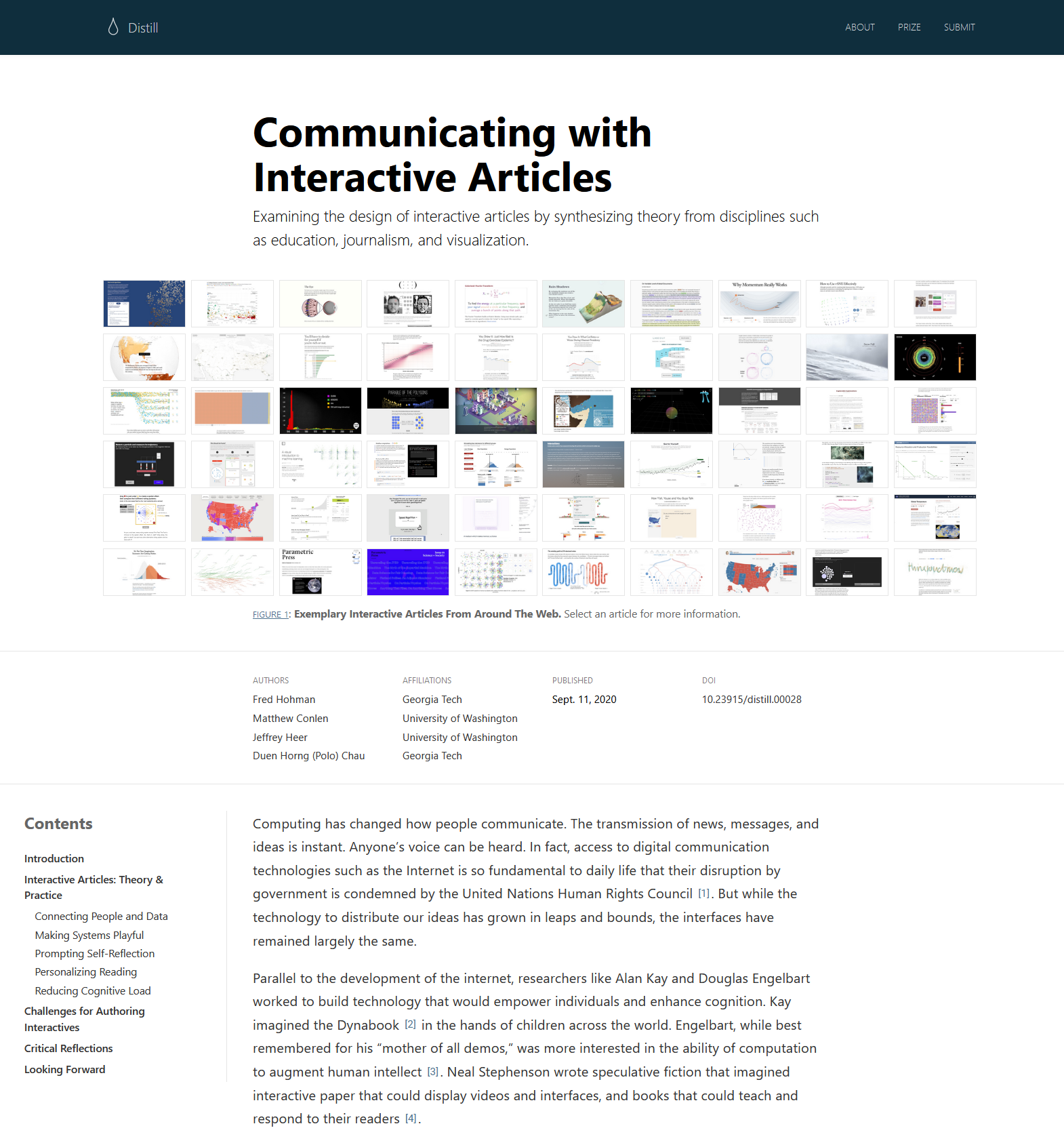
Tiny systems and ML
(Distill, 2016-2021)
Five affordances of interactive articles
Connecting people & data
Making systems playful
Prompting self-reflection
Personalizing reading
Reducing cognitive load

Write your own tiny programming system(s)
Programming languages and systems
Tomas Petricek, Charles University
tomas@tomasp.net
@tomasp.net
https://tomasp.net
https://d3s.mff.cuni.cz/teaching/nprg077


Programming Languages
Programming is
writing code
Formal semantics, implementation, paradigms, types
We know how
to study this!

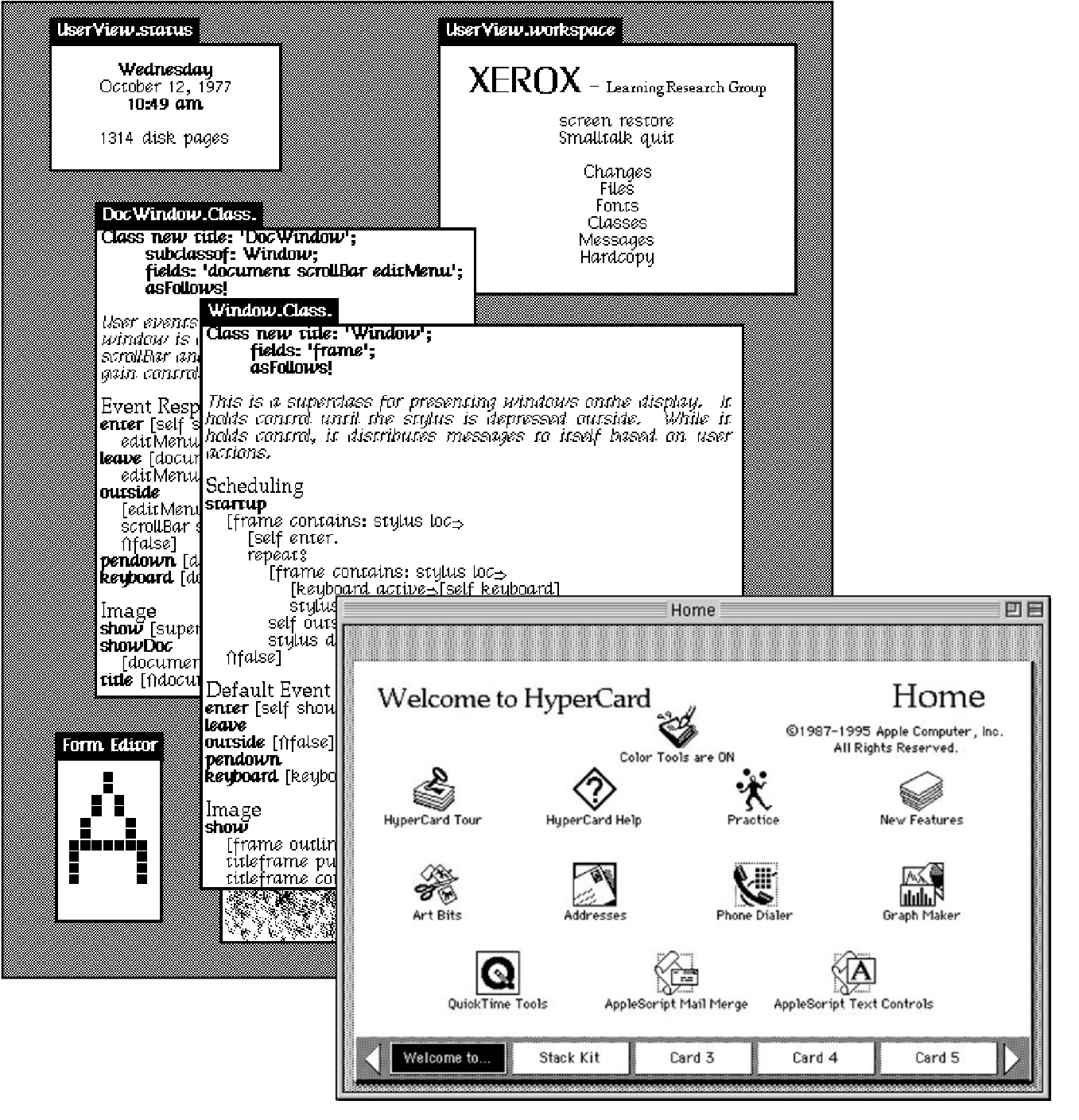
Programming Systems
Interacting with a stateful system
Feedback, liveness, interactive user interfaces
But how do we
study this?

Paradigm shift in 1990s

From systems to languages
- From running system to code
- From state & interaction to semantics
- Incommensurable ways of thinking!
History of science matters!
- How did we get where we are?
- What ideas got lost along the way?
- How to recover them?

Language paradigms
-
Functional programming
No mutable state, everything a function -
Imperative programming
Mutable memory with pointers -
Object-oriented programming
Everything an object, hides its own logic -
Logic programming
Declare facts and use inference

Demo
Logic programming in Prolog

System interaction
-
Command line programming systems
Code editor, compiler, build tools, etc. -
Image-based programming model
Programming system is always running -
Interactive and live programming
System provides continuous feedback -
Incremental or reactive evaluation
Recompute on edit or when new data come

Demo
Object-orientation in Smalltalk

What really matters?
Static structure (program)
- Source code of the program
- What you have at the start
Dynamic structure (process)
- Runtime data structures
- What else do you need to run
Logic of evaluation (execution)
- How the dynamic state evolves?

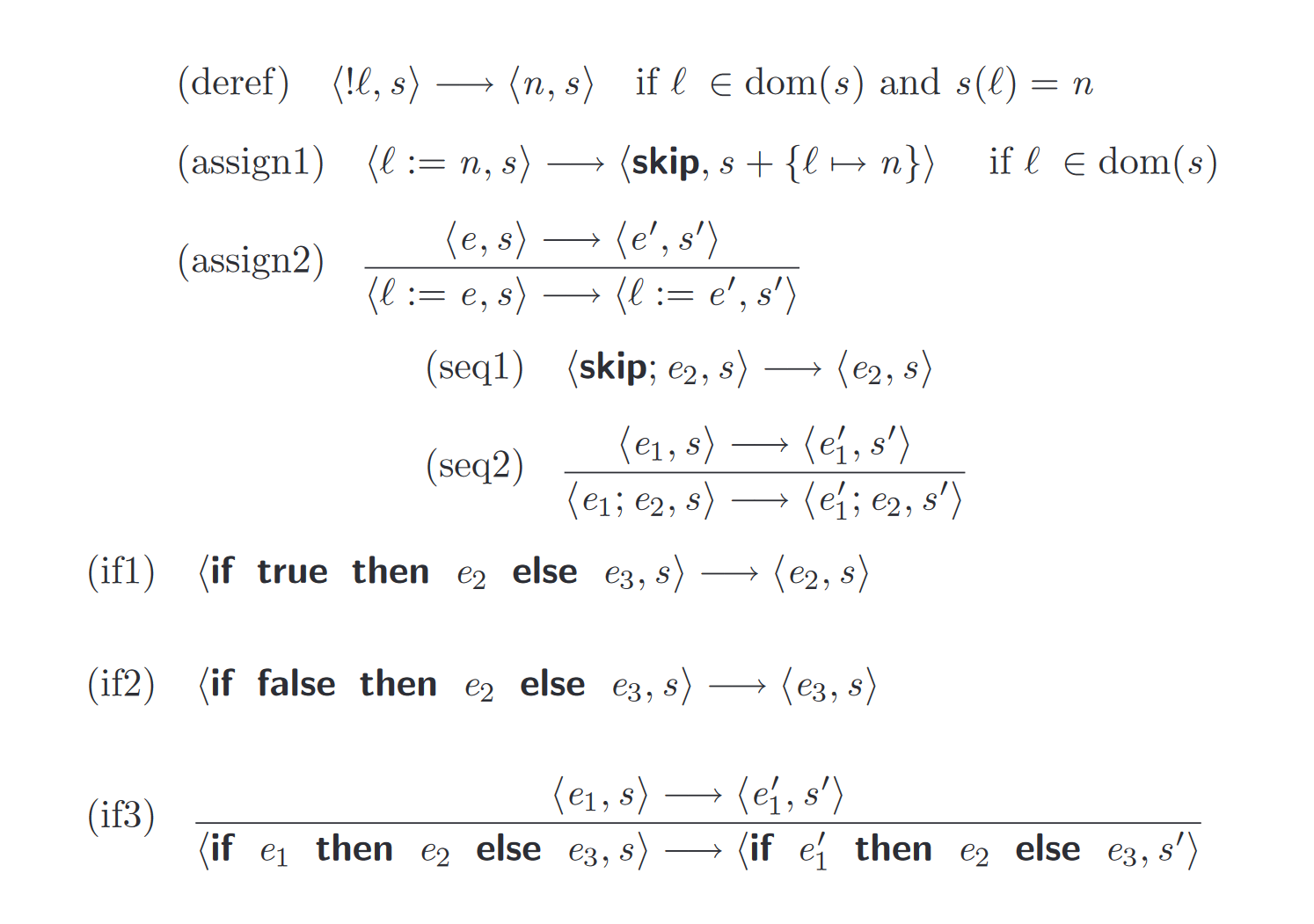
Operational semantics
Standard approach
to programming language theory
Why write small interpreters instead?

(* A term like 'father(william, X)'
consists of predicate 'father',
atom 'william' and variable 'X' *)
type Term =
| Atom of string
| Variable of string
| Predicate of string * Term list
(* A rule 'head(...) :- body.' *)
type Rule =
{ Head : Term
Body : Term list }
(* A program is a list of rules *)
type Program = Rule list
Code can run!
A good way to explain the structures!
1) Functional data types for the static and dynamic structure
2) A function to model the evaluation logic

Write your own tiny programming system(s)
A tase of the F# language
Tomas Petricek, Charles University
tomas@tomasp.net
@tomasp.net
https://tomasp.net
https://d3s.mff.cuni.cz/teaching/nprg077


The F# programming language

What is F# about?
- Functional-first based on OCaml
- Great interop with .NET and JS
- Open-source (MIT) with team in Prague!
Who uses F# for what?
- Consultancies for full-stack web dev
- Finance and insurance companies for modelling
- TU Kaiserslautern for systems biology
- Success stories like Jet.com

Why F#?
Building tiny programming systems
- Algebraic data types for structure modelling
- Mostly functional is great for logic
- Runs everywhere & has nice tools
- I like the language and can help you!

Demo
First look at F#

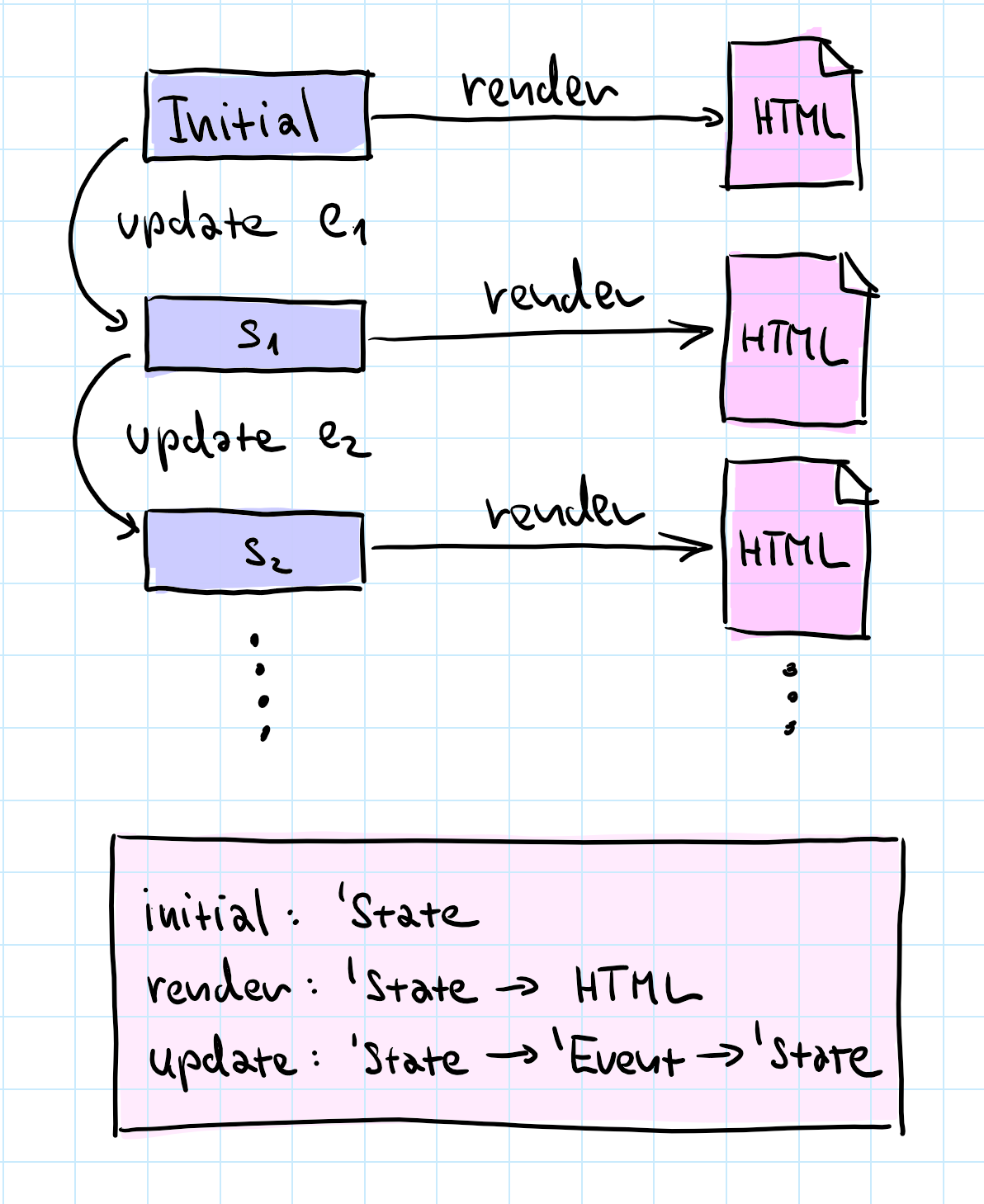
Elmish architecture
Functional interactive user interface development
Types for application
State and user Event
Functions to render
and update state

Demo
Building a counter in F#

Demo
Building a TODO list in F#

More about F#
We will only need a small part of the language!
I will introduce all constructs we will need as we go...

References
Tiny system examples
- Coeffects: Context-aware programming languages
- The Gamma: Democratizing data science
- The Lost Ways of Programming: Commodore 64 BASIC
Starting points
- Ingalls, D. (2020). The Smalltalk Zoo: Smalltalk-78 (NoteTaker)
- Hohman, F. et al. (2020). Communicating with Interactive Articles
- Schank, R. C., Riesbeck, C. K. (1981). Inside Computer Understanding Five Programs Plus Miniatures
- Kamin, S. (1990) Programming languages: an interpreter-based approach. Addison-Wesley.
- Kamin, S. (1990) PLIBA source code mirror on GitHub
- Sack. W. (2020). Miniatures, Demos and Artworks: Three
Kinds of Computer Program, Their Uses and Abuses
